- Screen-printed transfers and laser cut transfers for customizing your professional textiles !
- My account
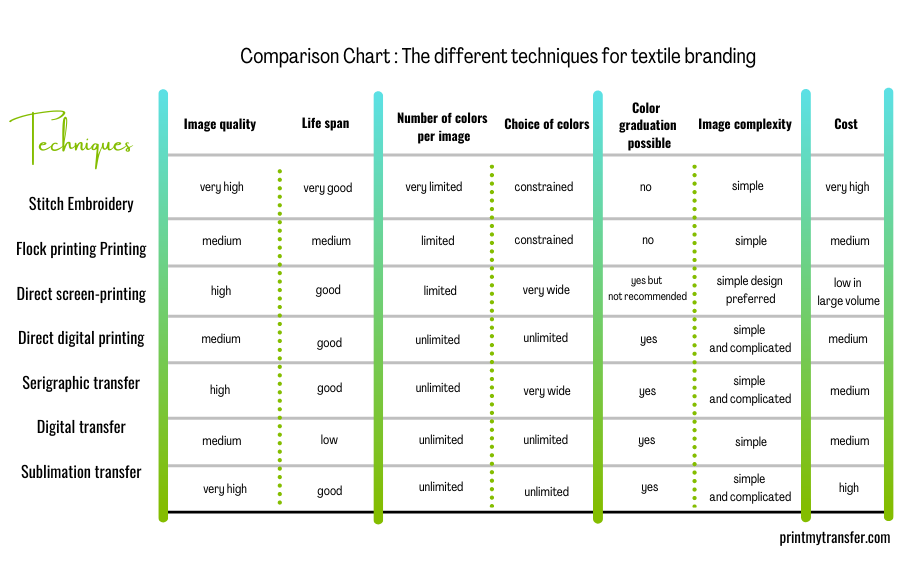
Comparison Chart 2020: The different techniques for textile branding
Each method of textile branding has its advantages and disadvantages. The choice will depend upon your goals and requirements in terms of textile branding.
Stitch Embroidery, what is it?
Stitch Embroidery involves creating the visual image with needles and stitch.
This traditional technique provides a particularly pleasing raised aesthetic which is greatly appreciated in luxury textile branding. The stitch penetrates through the support material, thus is not recommended for waterproof garments or light weight fabric.
Advantages of stitch embroidery:
- Good longterm durability
- High quality, elegant finish
Disadvantages of stitch embroidery:
- Relatively costly
- Longer production time
- Cannot incorporate colour blending or colour graduation
- Difficult to produce certain details
- No exact match to Pantone colours
Flock printing, what is it ?
Flock printing, or flocking (flex in french), is the textile printing technique best known to the public through its recurrent use in sport (numbers, names on shirts...).
This technique involves machine cutting an image directly from a roll of thermo adhesive coated coloured vinyl. The vinyl cut-out is then applied to the textile by heat press. There are two types of flocking: Standard monochrome flocking, and printed flocking where a multi-colour image is printed on the vinyl prior to cutting out from the sheet.
Flocking is most often used for personalising textiles with a simple image and few colours. It is well suited to small and medium quantity production runs.
Advantages of flock printing on textiles:
- No minimum order size
- Individual numbering is possible
- Technique viable on all textile types
- Reasonable durability
Disadvantages of flock printing on textiles:
- non-elastic
- Colour gradients and special colours not possible
- Fine or sharp details not possible
- Requires cutting out (equipment purchase, time...)
Direct screen-printing
Direct screen-printing, or serigraphy, is an artisanal technique where a mesh is used to transfer ink onto a textile, except in areas made impermeable to the ink by a blocking stencil.
One colour is printed at a time, so several screens are required to produce a multi-coloured image. The ink is pressed directly onto the fabric through the mesh and is absorbed into the fibres.
Direct screen-printing is well suited to high quality branding using relatively simple graphics and few colours.
Advantages of direct screen-printing:
- High quality image with good colour reproduction
- Very good resistance to washing
- Low cost, decreasing with quantity
Disadvantages of direct screen-printing:
- Image quality reduces as image complexity increases
- Colour graduations not possible
- Minimum order size will depend upon complexity and number of colours
- Maximum wash temperature of 40ºC
Direct digital printing, what is it ?
Direct digital printing uses ink jet printing to create an image directly on the textile support. The ink is absorbed directly by the fabric. This branding technique is recommended for photos or large images comprising numerous colours, and for small or medium quantities.
Advantages of direct digital printing:
- Clean and precise image quality
- Large format printing (37cm x 47cm)
- long life span
- Rapid production
Disadvantages of direct digital printing:
- Textile support should have be minimum 70% cotton content to ensure good performance
- Colours a little less vivid on white fabrics
- Pantone colour accuracy not possible
- Relatively high cost on dark fabrics
Serigraphic transfer, what is it ?
Serigraphic transfer involves laying plastisol (suspension of polymer particles in a liquid plasticiser) on a paper support. This printing method, whilst using mesh screens, is an ideal alternative to direct screen-printing because this technique allows the use of different mesh sizes to enable fine detail.
After the last layer of ink is applied, the image is sealed with an adhesive to create a thermal transfer. Using a thermal press, the image is applied to the fabric.
Serigraphic transfer is particularly well suited to commercial marketing.
Advantages of serigraphic transfer:
- Technique offering high quality results with excellent colour control
- Full colour spectrum available - Very good life span and resistance to washing
- Easy application on all supports
- Complex, detailed images are viable
Disadvantages of serigraphic transfer:
- Final result relies upon the image quality supplied by the client
- Colour graduations limited to flat colours on a white foundation
Digital transfer, what is it ?
Digital transfer, or digital flocking, involves ink jet printing an image onto an adhesive film. Once printed, the excess needs to be trimmed from around the edges. The image is then transferred to the textile support using a thermal press.
This technique is best suited to small quantities requiring quick branding on publicity items.
Advantages of digital transfer:
- unlimited colours
- Colours can be graduated
- Inexpensive for small quantities
Disadvantages of digital transfer:
- Colour fade is quicker than with other techniques
- Fragile and short life span
- Plastic effect on larger images
Sublimation transfer, what is it?
Sublimation transfer is a recent technique using a top quality dedicated printer for dye-sublimation onto special paper. The image is then transferred to the textile support using a thermal press. The ink is thus infused directly into the fabric.
Sublimation transfer is essentially used on white or very lightly coloured fabrics. This technique is ideal for sports and high-performance clothing.
Advantages of sublimation transfer:
- High quality images on polyester, lycra...
- Good control of colours and contrast
- No drying time required
- Long life span since the ink is integrated into the fabric
Disadvantages of sublimation transfer:
- Constraints on fabric colour (no black)
- Long process
- Higher cost





